| Table of Contents |
|---|
Servos
Standard servos are used to maintain a certain angle, not meant for full rotation
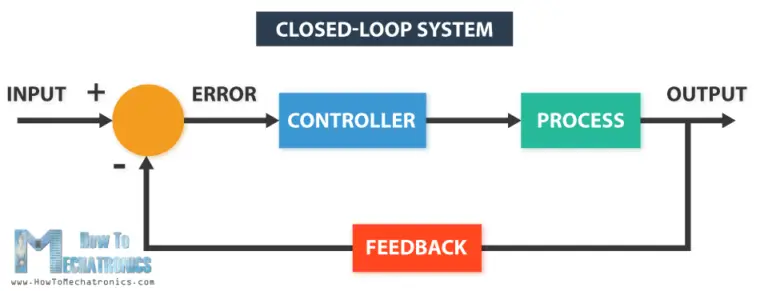
Uses closed-loop feedback control
Servos are used in applications requiring high torque, accurate rotation within a limited angle such as Robotic arms, valve control, rudder control etc.
...
...
SG90 Micro Servo
...
SG90 is a servo motor which operates based on PWM control signals
The servo maintains a certain angle (position) based on the width of the pulse fed in through a signal input
Some technical specifications
Weight: 9 g
Dimension: 22.2 x 11.8 x 31 mm approx.
Stall torque: 1.8 kgf·cm
Operating speed: 0.1 s/60 degree
Operating voltage: 4.8 V (~5V)
PWM frequency = 50Hz
Pin configuration: Yellow / Light Orange / White (Signal), Red / Dark Orange (+5V), Brown/Black (Ground)
...
Note : The pulse width in the image does not correspond to SG90, for illustration of the concept only.
...
544 – 1500 – 2400 us
0° – 90° – 180°
...
- Continuous rotation servos are normal servos modified to perform open loop speed control (instead of closed loop position control)
- Rotation speed and direction are controlled through PWM signals (pulse width) for continuous rotation servos, just like how position is controlled for standard servos
- Effectively, continuous servos are DC motors with integrated motor drivers and reduction gears in a compact, inexpensive package
- FS90R continuous rotation operating speed: 110RPM (4.8V); 130RPM (6V)
- Can continuous rotation servos be used to achieve accurate positioning without any additional hardware?
Servo Library
This library allows an Arduino board to control servo motors
.Standard servos allow the shaft to be positioned at various angles, usually between 0° and 180°
. Continuous rotation servos allow the rotation of the shaft to be set to various speedsAny digital pin on UNO can be used, not necessarily those supporting PWM. However, note that using Servo library disables analogWrite() functionality on pins 9 and 10
attach(int) - attach a servo to an I/O pin, e.g., servo.attach(pin), servo.attach(pin, min, max)
servo: a variable of type Servo, pin: pin number, default values: min = 544 us, max = 2400 us
write(int) - write a value to the servo to control its shaft accordingly
- Standard servo - set the angle of the shaft Continuous rotation servo - set the speed of the servo(0: full speed in a direction, 180: full speed in the other, and around 90: no movement)
- e.g., servo.write(angle), angle = 0 to 180
detach() - stop an attached Servo from pulsing its I/O pin
http://arduino.cc/en/Reference/Servo
C++ | Blocks | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
...
Caution : Do not overload the servo. The servo and your battery / power source could be damaged if the servo is overloaded.
Do not power the servo from a 9V battery. Most servos can’t take > 6V.
Continuous Rotation Servos
Continuous rotation servos are standard servos modified to perform open-loop speed control (instead of closed-loop position control)
Rotation speed and direction are controlled through PWM signals (pulse width) for continuous rotation servos, just like how the position is controlled for standard servos
Effectively, continuous servos are DC motors with integrated motor drivers and reduction gears in a compact, inexpensive package, rather than true 'servo' motors
Continuous rotation servos allow the rotation of the shaft to be set to various speeds
Electrical connections are identical to that of a standard servo.
The original servo library can be used; e.g., servo.write(angle), angle = 0 to 180 → 0: full speed in one direction, 180: full speed in the other, and around 90: no movement
FS90R (also known as SG90 continuous / 360o/ full rotation) operating speed: 110RPM (4.8V); 130RPM (6V)
Can continuous rotation servos be used to achieve accurate positioning without any additional hardware?